Monitoring Services Health
Chapter 8: Monitoring Services Health
A centralized dashboard for viewing the health of internal Redfish services across your infrastructure.
ℹ️ Service Monitoring
Available to: All user roles with monitoring permissions
Scope: Organization / Hierarchy View / POD levels
Permissions: Monitor service health status for authorized scope
Purpose: Fleet-wide Redfish service health monitoring across different management scopes
Overview: Your Fleet-Wide Systems Check
The MANAGE → Services page is your fleet-wide systems check for the internal management engine. While the Node Detail → Services tab focuses on a single node, this page provides a high-level, aggregated view. Its primary purpose is to help you diagnose issues with the management plane itself.
Scope-Based Visibility:
Organization scope: View service health across all PODs you have access to
Hierarchy View scope: View service health across PODs within the selected Hierarchy View
POD scope: View service health for nodes within the selected POD
If EDCC is having trouble communicating with one or more nodes, this is the first place to look to understand the scope of the problem. It helps you quickly answer key questions depending on your selected scope:
Organization/HV level: "Is there a widespread service issue affecting multiple PODs?"
POD level: "Is there a widespread service issue affecting multiple nodes in this POD?"
All levels: "Is this a systemic problem or an isolated incident?"
Understanding Scope-Based Monitoring
How Scope Affects Service Monitoring
The services you see on this page depend on your currently selected management scope. This dynamic filtering helps you focus on the relevant infrastructure without being overwhelmed by nodes outside your current context.
Scope Selection Examples:
Organization
All nodes from all authorized PODs
Global infrastructure health check across entire organization
Hierarchy View
All nodes from PODs within selected HV
Regional data center monitoring (e.g., "East Coast HV" shows POD1, POD2, POD3)
POD
All nodes within selected POD
Detailed investigation of specific POD issues
Permission Filtering:
User with POD1, POD3, POD5 access:
• Select "Organization" → See nodes from POD1 + POD3 + POD5
• Select "HV1" (contains POD1,2,3,4,5) → See nodes from POD1 + POD3 only
• Select "POD1" → See nodes from POD1 onlyScope Navigation Tip: Use the hamburger menu (top-left) to switch between Organization, Hierarchy View, and POD scopes. The header always shows your current selection.
The Monitoring & Triage Workflow
The interface is designed for a simple, two-step workflow: first, get a high-level overview from the status list, then use the powerful filtering and action tools to investigate specific problems.
Select Scope Flest Status Overview Filter Problem Nodes Investigate Individual Issues
Multi-Scope Investigation Pattern
Top-Down Approach (Recommended for widespread issues):
Organization view: Identify which PODs are affected
Narrow to HV: Focus on specific regional or logical groupings
Drill to POD: Investigate specific node issues
Node Detail: Deep-dive individual server diagnostics
Targeted Approach (For known issues):
Direct POD selection: Jump straight to affected POD
Filter critical nodes: Isolate problem servers
Use quick actions: Navigate to diagnostic pages
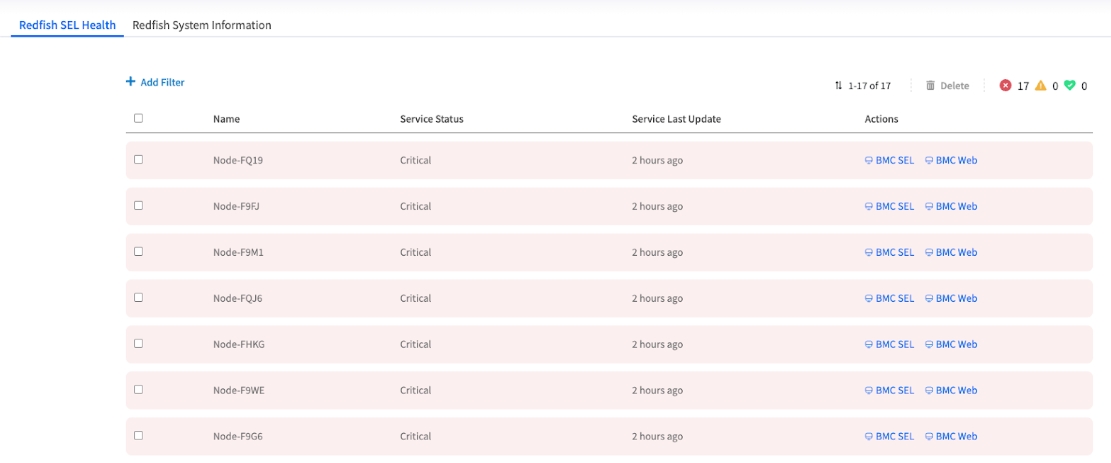
Reading the Node Service Status List
Overview: This table is your main dashboard, acting as a "fleet status board" for the selected service. Each row represents a node, and each column gives you a piece of critical diagnostic information. It allows you to spot systemic issues at a glance, for example, if a recent network change has impacted communication for multiple nodes across different PODs.
Name
Identifier: The unique name of the node.
Node identification
Service Status
The Key Indicator: This shows the current health of the selected service on that node (Critical, Good). The entire row is color-coded, so you can spot failing nodes instantly.
PRIMARY - Immediate health status
Service Last Update
The "Heartbeat" Timestamp: This shows the last time EDCC successfully received a status update from this service. A stale or old timestamp is a major red flag, indicating a potential network issue or an unresponsive BMC.
CRITICAL - Communication health
Actions
Your Investigation Shortcuts: These are dynamic, context-aware links designed to take you directly to the most relevant page for troubleshooting that specific service failure.
TOOLS - Direct investigation paths
Key Monitoring Indicators
Service Status Priority:
Critical (Red): Immediate attention required - service failure detected
Good (Green): Service operating normally
Missing Status: Possible communication failure
Service Last Update Analysis:
Recent Timestamp: Normal communication with BMC
Stale Timestamp: Warning sign of network or BMC issues
Missing Timestamp: Communication completely broken
Cross-Scope Pattern Recognition
What to Look For:
Organization view: Are problems concentrated in specific PODs?
Hierarchy View: Are issues affecting one region more than others?
POD view: Are problems clustered on specific racks or network segments?
All scopes: Are similar services failing across multiple nodes?
Filtering and Investigating
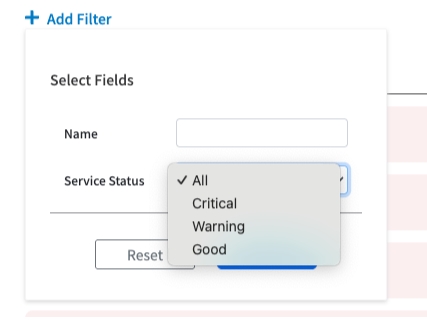
Filtering for Problem Nodes
In a large deployment with hundreds of nodes across multiple PODs, the filter is your most essential tool. It allows you to cut through the noise and instantly isolate the nodes that need attention, regardless of your current scope.
Process:
Click the + Add Filter button
Filter the list by Name or Service Status
Click Apply
Common Filter Scenarios by Scope:
Organization/HV Scope:
Critical Status Only: Find all critical nodes across multiple PODs
POD-Specific Issues: Filter by node names containing POD identifiers
Stale Updates: Identify communication problems across infrastructure
POD Scope:
Critical Status Only: Focus on nodes requiring immediate attention
Rack-Based Filtering: Filter by naming patterns for specific racks
Service Type Issues: Isolate specific service failures
Using Quick Actions to Drill Down
The Actions column provides the most efficient path from problem detection to root cause investigation. These shortcuts are designed to minimize "context switching" by providing a direct, one-click path to the most relevant diagnostic page.
Action Options by Service Type:
Redfish SEL Health
BMC SEL, BMC Web
Jump to event logs or native BMC interface
Redfish System Information
System Info, BMC Web
Access hardware details or BMC interface
Investigation Path:
Flest View Problem Quick Action Node-Level Diagnostics Root Cause Resolution
Cross-Scope Navigation: Quick Actions work the same way regardless of your selected scope, always taking you to the specific node's diagnostic page.
Managing Service Events
Understanding the Batch "Delete" Action
This function is an administrative tool for managing the user interface, not the nodes themselves. After you have resolved a widespread service issue, you can use this batch action to clear the resolved Critical status indicators from this screen in a single operation.
Important: This is Not a Node Deletion
The Delete button on this page DOES NOT remove the node from the POD. It is purely an administrative action for clearing the selected service event records from this UI screen only.
When to Use Delete Action:
After Issue Resolution: Clear resolved service alerts from the display
UI Cleanup: Remove outdated status indicators after maintenance
Event Management: Maintain clean service status overview
Works Across All Scopes: Clean up events regardless of Organization/HV/POD selection
What Delete Does NOT Do:
Remove nodes from POD
Delete actual service configurations
Affect node functionality
Remove nodes from other EDCC functions
Change your current scope selection
Chapter Summary & Key Takeaways
Multi-Scope Monitoring: This page works across Organization, Hierarchy View, and POD scopes - not POD-only
Dynamic Visibility: What you see depends on your selected scope and user permissions
Use This Page for Fleet-Wide Issues: Best for spotting problems that affect multiple nodes across your authorized infrastructure
Last Update is a Key Indicator: A stale timestamp can be a sign of a network or BMC connectivity issue, even if the status is "Good"
Actions are Your Shortcuts: Use the Actions column to jump directly from fleet-level alerts to node-level diagnostic pages
Delete Clears the View, Not the Node: The batch Delete action is for UI cleanup only and does not affect nodes or your scope selection
Pattern Recognition: Look for patterns across multiple nodes and PODs to identify systemic issues vs. isolated problems
Scope Switching: Use the hamburger menu to navigate between different scopes for top-down or targeted investigation
What's Next: Chapter 9 will explore POD View topology management, where you'll learn to visualize and organize your infrastructure layout.
💡 Pro Tip: Use Organization or HV scope as your first stop when Dashboard shows widespread health issues - it quickly reveals whether problems are affecting specific PODs or multiple systems across your infrastructure. Then narrow your scope to investigate specific problem areas.